Application of Electrical Cabinets in Building Automation
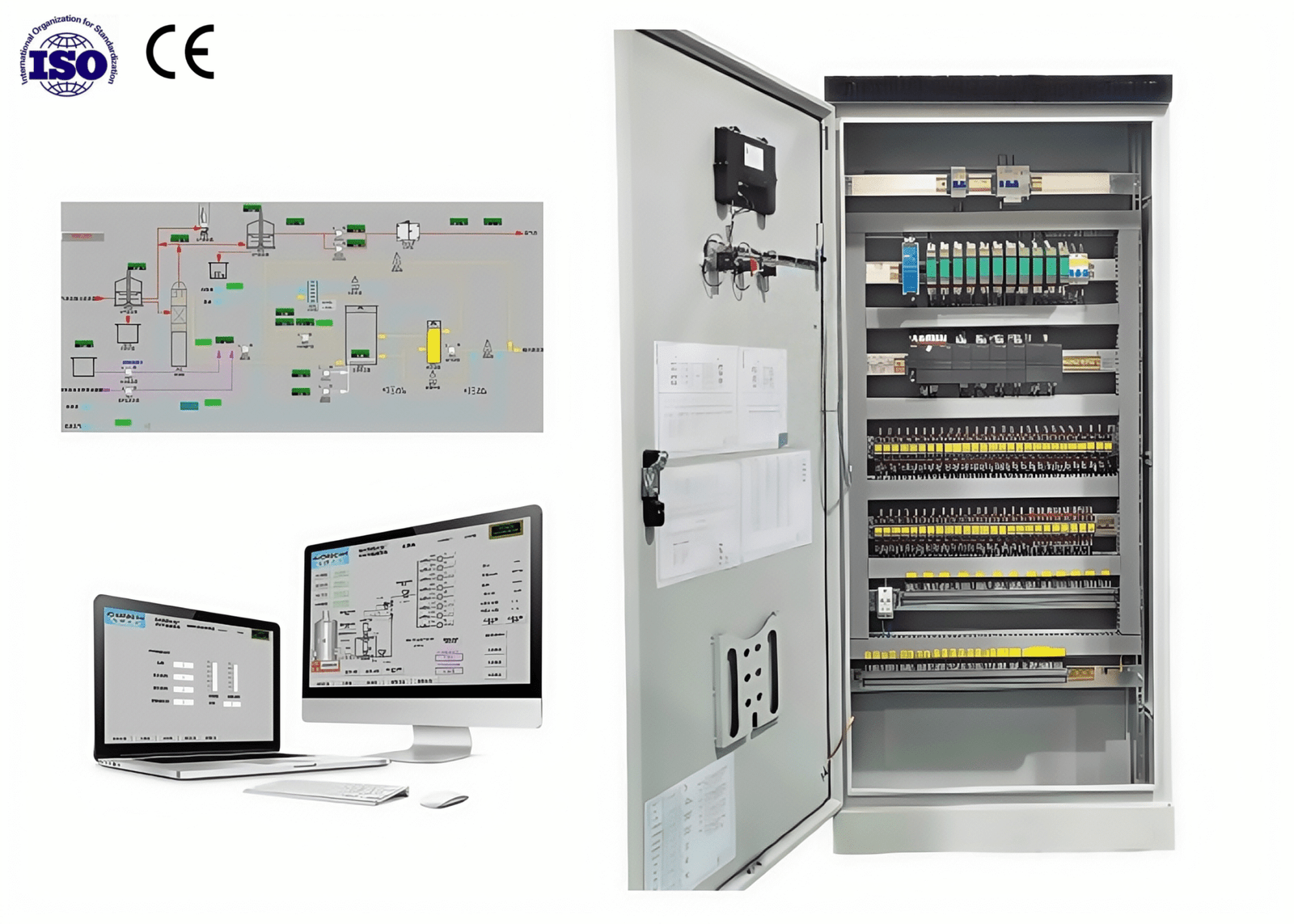
1. Introduction
In modern smart building ecosystems, the Building Automation System (BAS) acts as the central nervous system, responsible for equipment coordination, dynamic energy management, and precise environmental control. Electrical cabinets, as the physical 载体 and functional core of BAS, are indispensable—they not only integrate controllers, actuators, and communication modules but also serve as the hub for centralized interaction of information flows, energy streams, and control commands within buildings.
From lighting and HVAC to water supply and security systems, electrical cabinets permeate all building subsystems, forming the hardware foundation for centralized management and automated operation of smart buildings. Their technical performance and intelligence directly determine the overall operational efficiency, energy consumption, and safety of buildings, making them key infrastructure for the transformation from “traditional operation” to “smart management.”
2. Core Categories and Functional Analysis
2.1 Power Distribution Cabinet
As the “nerve node” of a building’s electrical system, the power distribution cabinet centrally controls and protects load circuits, integrating circuit breakers, contactors, isolators, surge protectors, etc. It enables remote switching, real-time fault alarms, and electricity consumption data collection.
Key Highlights:
- Adopts zoned power distribution design for rapid fault localization and isolation, enhancing system fault tolerance;
- Seamlessly integrates with energy management platforms to enable power statistics, peak-valley regulation, and energy efficiency analysis;
- Modular structure allows flexible expansion of circuits based on load growth, reducing renovation costs.
2.2 Fan Control Cabinet
Designed for ventilation equipment such as fresh air fans, supply fans, and exhaust fans, this cabinet controls start/stop, stepless speed adjustment, and operation mode switching. It can also link with CO₂ sensors and PM2.5 monitors to adjust airflow on demand, balancing indoor air quality and energy consumption.
Key Highlights:
- Equipped with Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) for over 30% energy savings through smooth speed regulation;
- Supports preset interlock logic (e.g., “occupancy-based ventilation”), automatically increasing airflow when occupied and reducing speed when vacant;
- Real-time monitoring of fan current and temperature, with automatic shutdown and alarm notification in case of abnormalities, minimizing equipment wear.
2.3 Pump Control Cabinet
Widely used in HVAC water circulation, domestic water supply, and fire sprinkler systems, it manages sequential startup, rotational operation, frequency conversion, and closed-loop liquid level control of pumps to ensure stable water pressure and efficient system operation.
Key Highlights:
- Features multi-pump rotation logic to avoid uneven wear from single-pump long-term operation, extending equipment lifespan by over 30%;
- Integrates PLC-based intelligent control to dynamically adjust speed based on pipeline pressure and flow, reducing water transportation energy consumption;
- Equipped with multiple protection functions (phase loss, overload, dry running) and automatic switchover to backup pumps during faults, ensuring system continuity.
2.4 Lighting Control Cabinet
As the “central dispatcher” of building lighting systems, it supports timing control, zoning management, sensor linkage (e.g., infrared/microwave sensing), and scene mode switching (e.g., “working mode,” “energy-saving mode”), ideal for large spaces like office buildings and commercial complexes.
Key Highlights:
- Compatible with KNX/DALI protocols for precise single-lamp control and complex scene programming;
- Integrates light sensors for “daylight harvesting,” automatically adjusting artificial lighting brightness to achieve 40% energy savings;
- Connects to BMS platforms for global monitoring, supporting faulty lamp localization and energy consumption analysis.
2.5 RCU Room Control Unit
Designed for hotels and high-end apartments, it integrates control of room lighting, HVAC, curtains, and sockets. It links with door lock systems and PMS (Property Management Systems) to enable smart scenarios such as “automatic service activation upon check-in” and “energy-saving mode on departure.”
Key Highlights:
- Synchronizes real-time room status (occupied/vacant) with PMS, automatically switching operation modes (e.g., turning off main lights and lowering AC power in vacant rooms);
- Supports dual control via local touchscreens and mobile APPs, balancing guest convenience and hotel management needs;
- Built-in service response modules (e.g., “room cleaning,” “emergency call”) to optimize room service workflows.
2.6 Energy Monitoring Cabinet
Acting as the building’s “energy manager,” it collects real-time data on electricity, water, gas, and heating/cooling consumption via smart meters. Processed data is uploaded to energy efficiency platforms, providing insights for energy-saving strategies.
Key Highlights:
- Samples data every 15 minutes, supporting hourly, daily, and monthly energy trend analysis with year-on-year/quarter-on-quarter comparisons;
- Built-in anomaly detection algorithms to automatically alert on excessive energy use or pipeline leaks, reducing waste;
- Interfaces with carbon emission accounting systems to generate carbon footprint reports, aiding buildings in achieving “dual carbon” goals.
3. Technological Breakthroughs and Highlights
- High Integration and Modular Design
Breaking free from traditional “decentralized layouts,” optimized structures integrate controllers, power modules, and communication interfaces into compact spaces, reducing footprint by over 50%. Modular components allow on-demand function combinations (e.g., “distribution + monitoring,” “control + communication”), significantly shortening installation and commissioning time. - Full Protocol Compatibility and Interconnectivity
Equipped with multi-protocol conversion modules, it supports Modbus, BACnet, KNX, and LonWorks, enabling seamless integration with BAS, EMS, and IBMS platforms for cross-system data sharing and collaborative control. - Intelligent Maintenance and Remote Management
Integrated with PLC and HMI, it supports local parameter configuration and status monitoring. Via 4G/5G or Ethernet, maintenance personnel can remotely diagnose faults, upgrade programs, and adjust control logic, reducing response time from hours to minutes. - Environmental Adaptability and Safety Redundancy
Customized protection for diverse scenarios: industrial-grade cabinets with IP65 rating for humid/dusty environments; 316 stainless steel + anti-corrosion coatings for coastal areas; dual-cabinet redundancy in critical settings (e.g., data centers) to ensure uninterrupted operation during single-point failures. - Customization and Scene Adaptability
Tailors dimensions, internal layouts, and component selections to building types (commercial, hospitals, airports), space constraints (shafts, mezzanines), and functional needs (explosion-proof, silent). For example, hospital operating room cabinets meet EMC and cleanliness standards.
4. Profound Impact and Value in Modern Architecture
- Driving Building Energy Efficiency Revolution
Through precise control and energy monitoring, electrical cabinets help buildings achieve 30%-50% energy savings. For instance, a commercial complex reduced annual electricity use by 800,000 kWh with smart lighting cabinets; hotels cut vacant room energy consumption by 60% via RCU control. - Ensuring Building Operational Safety
Overload and short-circuit protection in distribution cabinets prevent electrical fires; fire-linked logic in pump cabinets ensures rapid activation of sprinkler systems; leak alerts in energy monitoring cabinets avoid water pipe bursts, strengthening building safety. - Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Remote monitoring and smart alarms reduce on-site inspections—an office building cut maintenance staff by 40% with intelligent fan cabinets. Automatic fault localization shortened Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) from 4 hours to 1 hour, minimizing downtime losses. - Supporting Smart City Development
As “terminal nodes” for building data collection, electrical cabinets upload energy consumption and equipment status to city-level platforms, providing foundational data for smart grid dispatch, regional energy optimization, and emergency management, driving buildings from “individual intelligence” to “urban synergy.”
